The Automatic Identification System (AIS) is one of the most critical advancements in modern maritime navigation. This globally implemented system allows ships to communicate their position, speed, and other essential information in real-time, contributing to the safety and efficiency of maritime operations. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the significance of AIS, its functions, the different types of AIS systems, and how it continues to transform the global maritime industry.
Content:
1. What is the Automatic Identification System (AIS)?
2. How Does AIS Work?
3. Types of AIS Systems
4. Benefits of AIS in Maritime Operations
5. Challenges and Limitations of AIS
6. The Role of AIS in Future Maritime Technologies
7. AIS and Global Maritime Security
8. Conclusion
9. FAQs
1. What is the Automatic Identification System (AIS)?
2. How Does AIS Work?
3. Types of AIS Systems
- Class A AIS
- Class B AIS
- AIS Base Stations and Satellite AIS
4. Benefits of AIS in Maritime Operations
- Collision Avoidance
- Traffic Monitoring and Control
- Search and Rescue Operations
- Environmental Monitoring and Protection
- Operational Efficiency
5. Challenges and Limitations of AIS
- AIS Signal Range and Reliability
- Overcrowding of AIS Channels
- AIS Data Vulnerability
- Over-reliance on AIS for Navigation
6. The Role of AIS in Future Maritime Technologies
- Autonomous Ships and AIS
- Big Data and Predictive Analytics
- Integration with Environmental Monitoring Systems
7. AIS and Global Maritime Security
- Anti-Piracy Efforts
- Combatting Illegal Fishing
- Border Security and Surveillance
8. Conclusion
9. FAQs

1
What is the Automatic Identification System (AIS)?
The Automatic Identification System (AIS) is an automated tracking system used primarily on ships and vessels to enhance navigation safety. AIS works by transmitting vessel information, such as identity, position, speed, course, and other data, to nearby ships, coastal authorities, and traffic monitoring centers.
The system operates over VHF radio frequencies, using transponders to send and receive data between vessels. AIS was originally developed as a tool to avoid collisions by providing situational awareness, but its applications have since expanded to include monitoring, traffic control, search and rescue operations, and environmental protection.
AIS is mandatory for all vessels over 300 gross tons on international voyages, cargo ships over 500 gross tons, and all passenger ships, as required by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) under the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS).
The system operates over VHF radio frequencies, using transponders to send and receive data between vessels. AIS was originally developed as a tool to avoid collisions by providing situational awareness, but its applications have since expanded to include monitoring, traffic control, search and rescue operations, and environmental protection.
AIS is mandatory for all vessels over 300 gross tons on international voyages, cargo ships over 500 gross tons, and all passenger ships, as required by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) under the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS).

2
How Does AIS Work?
AIS transponders on ships automatically broadcast key information at regular intervals. The data is sent via VHF radio waves to other ships, base stations, or satellites within range. The core information transmitted by AIS includes:
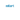
By receiving this information, ships and coastal stations can track vessel movements, predict potential collisions, and provide real-time traffic monitoring in congested waters. AIS data is displayed on shipboard systems such as Electronic Chart Display and Information Systems (ECDIS), providing navigators with a clear picture of the surrounding traffic and any potential hazards.
- Ship’s Name
- Maritime Mobile Service Identity (MMSI) Number
- Position (latitude and longitude)
- Speed Over Ground (SOG)
- Course Over Ground (COG)
- Ship Type and Size
- Destination and Estimated Time of Arrival (ETA)
By receiving this information, ships and coastal stations can track vessel movements, predict potential collisions, and provide real-time traffic monitoring in congested waters. AIS data is displayed on shipboard systems such as Electronic Chart Display and Information Systems (ECDIS), providing navigators with a clear picture of the surrounding traffic and any potential hazards.

Displaying ais targets using mKart MEGA ECDIS

3
Types of AIS Systems
AIS systems are generally classified into two main categories, Class A and Class B, depending on the type of vessel and its operational needs.
1. Class A AIS
Class A AIS is mandatory for larger ships, including commercial cargo vessels, tankers, and passenger ships. These transponders broadcast at higher power levels (up to 12.5 watts) and provide more frequent data updates. They are designed to handle the high traffic loads typically seen in busy shipping lanes or congested port areas.
Key features of Class A AIS include:
Key features of Class A AIS include:
- Faster update rates, with position reports every 2-10 seconds when underway.
- Advanced data output, including navigational status and detailed voyage information.
- More robust collision avoidance tools and integration with ship control systems.
2. Class B AIS
Class B AIS is intended for smaller vessels, such as recreational boats and fishing vessels. These transponders operate at lower power (2 watts) and have less frequent update intervals, typically transmitting every 30 seconds when underway. While not as comprehensive as Class A systems, Class B AIS still provides essential data for safe navigation.
Key features of Class B AIS include:
Key features of Class B AIS include:
- Lower power consumption, making it suitable for small vessels.
- Cost-effective compared to Class A transponders.
- Fewer data points transmitted, focusing on basic vessel information.
3. AIS Base Stations and Satellite AIS
In addition to shipborne transponders, AIS Base Stations are used by coastal authorities to monitor vessel traffic. These shore-based systems collect AIS data from passing ships and provide information to Vessel Traffic Services (VTS) for management and control of maritime traffic, especially in congested areas.
Satellite AIS (S-AIS) takes the system further by extending AIS coverage beyond the line-of-sight range of VHF radio waves. Satellite AIS enables the tracking of vessels in remote areas, such as the open ocean, where traditional coastal AIS systems are ineffective.
Satellite AIS (S-AIS) takes the system further by extending AIS coverage beyond the line-of-sight range of VHF radio waves. Satellite AIS enables the tracking of vessels in remote areas, such as the open ocean, where traditional coastal AIS systems are ineffective.

4
Benefits of AIS in Maritime Operations
The Automatic Identification System (AIS) offers several critical benefits for the maritime industry, from improving navigational safety to enhancing operational efficiency.
1. Collision Avoidance
The primary function of AIS is to prevent collisions by giving ships real-time information about the location, speed, and course of nearby vessels. AIS allows for improved situational awareness, especially in poor visibility conditions, such as fog, night-time operations, or heavy traffic areas.
2. Traffic Monitoring and Control
AIS provides detailed insights into vessel movements, helping Vessel Traffic Services (VTS) monitor and manage maritime traffic. This is particularly important in busy waterways like the English Channel, the Strait of Malacca, or around major ports. With AIS, authorities can ensure that ships adhere to traffic separation schemes, prevent bottlenecks, and quickly respond to potential accidents.

The Strait of Malacca is a crucial maritime passage connecting the Indian Ocean to the Pacific, located between Malaysia and the Indonesian island of Sumatra. The strait is approximately 900 km long and narrows to about 2.8 km at its narrowest point near Singapore. It is one of the busiest shipping lanes in the world, handling about 25% of global trade. The strait holds strategic importance for international trade, particularly for the transport of oil from the Middle East to East Asia. The Strait of Malacca is known for its challenging navigational conditions due to its narrow width, heavy traffic, and risks of piracy.
The English Channel is a narrow strait separating the southern coast of England and the northern coast of France. It connects the North Sea to the Atlantic Ocean and is about 560 km long, with a minimum width of 34 km at the Strait of Dover. The English Channel is one of the busiest shipping routes in the world, playing a crucial role in international trade and maritime transport. It also holds historical significance, serving as a natural barrier in military conflicts such as the Napoleonic Wars and World War II. The Channel Tunnel, known as the "Eurotunnel," runs beneath it, linking the UK with mainland Europe.
3. Search and Rescue Operations
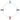
In emergency situations, AIS plays a crucial role in Search and Rescue (SAR) efforts. The system allows rescue coordinators to pinpoint the exact location of a vessel in distress, facilitating faster response times. Additionally, many AIS transponders are integrated with Man Overboard (MOB) alarms, ensuring that individuals lost at sea can be quickly located.

MOB coordinates are fixed with one click in mKart MEGA ECDIS


4. Environmental Monitoring and Protection
AIS helps authorities track the movement of ships carrying hazardous cargo, ensuring they follow designated routes to minimize the risk of accidents or environmental disasters. Moreover, AIS is used to monitor illegal activities such as illegal fishing, oil spills, and ship dumping, allowing authorities to take prompt action against violations.
5. Operational Efficiency
For shipping companies, the Automatic Identification System (AIS) offers substantial benefits in improving operational efficiency. By providing real-time tracking and data on vessel movements, AIS allows ship operators to optimize routes, minimize delays, and improve fuel consumption. Here are some ways AIS contributes to operational efficiency:
- Real-Time Fleet Monitoring: Shipping companies can track their entire fleet in real time, providing better control over logistics. AIS allows operators to monitor each vessel’s progress and make informed decisions on routing and timing adjustments to avoid delays.
- Optimized Route Planning: By using AIS data, vessels can plan their routes to avoid congested areas, adverse weather conditions, or potential hazards. This proactive approach reduces fuel consumption, shortens voyage times, and lowers operational costs. Some Voyage Management Systems (VMS) integrate AIS data with weather forecasting and ocean current information to further enhance routing efficiency.
- Port Operations Coordination: Ports use AIS to manage incoming and outgoing vessel traffic, ensuring that ships enter and leave harbors efficiently. Port authorities can schedule berth assignments more effectively, reducing turnaround times and preventing overcrowding at docks.
- Improved Maintenance Scheduling: Continuous monitoring of vessel movements via AIS provides insights into how ships are being operated. This data can help companies schedule predictive maintenance more effectively, addressing wear and tear issues before they become critical and avoiding unscheduled repairs that could lead to operational downtime.

5
Challenges and Limitations of AIS
While AIS offers many benefits, it is important to acknowledge the system's limitations and potential challenges.
1. AIS Signal Range and Reliability
AIS relies on VHF radio signals, which typically have a line-of-sight range of about 20 to 30 nautical miles. In areas with significant obstructions (such as tall buildings near ports or mountainous coastal regions), the signal may become weak or lost entirely. Furthermore, in open ocean areas, where there are no AIS base stations, AIS data must rely on satellite AIS (S-AIS) to extend coverage, which can sometimes be delayed or costly.
2. Overcrowding of AIS Channels
In heavily trafficked regions, the volume of AIS signals can overwhelm the available VHF channels, particularly for Class A AIS systems. This can lead to delays in receiving data or, in extreme cases, the loss of AIS messages. The introduction of Class B AIS systems, which have a lower priority for transmitting data, can further contribute to channel congestion in busy ports or narrow straits.
3. AIS Data Vulnerability
AIS data is broadcast openly and can be accessed by anyone with the proper receiving equipment. This raises potential security concerns, as malicious actors could exploit the system to track vessels for piracy or terrorism purposes. In addition, there is the risk of AIS spoofing, where false data is broadcast to mislead authorities or other vessels. The maritime industry continues to work on implementing cybersecurity measures to address these vulnerabilities.
4. Over-reliance on AIS for Navigation
While AIS is an invaluable tool for safe navigation, it should not be the sole method used by navigators. Bridge officers are trained to cross-reference AIS information with radar systems, visual observations, and paper charts when necessary. Over-reliance on AIS data, especially in congested areas, could lead to errors in judgment, particularly if data is not regularly updated or if signals are obstructed.

6
The Role of AIS in Future Maritime Technologies
As the maritime industry continues to evolve, AIS will play an increasingly important role in future developments and innovations.
1. Autonomous Ships and AIS
One of the most exciting frontiers in maritime technology is the development of autonomous vessels. These ships, controlled by artificial intelligence (AI), require continuous, real-time data to navigate safely and efficiently without human intervention. AIS will be a crucial part of these systems, providing real-time location data and information on nearby vessels. Autonomous navigation systems will integrate AIS data with advanced sensor technologies, radar, and ECDIS to operate vessels autonomously on international waters.
2. Big Data and Predictive Analytics
The data generated by AIS systems can be used as part of big data analysis to optimize global shipping operations. This data, when combined with machine learning algorithms, can predict trends in vessel traffic, identify bottlenecks, and optimize routes for faster, more fuel-efficient journeys. It can also be used to forecast maintenance needs based on vessel performance data, further improving operational efficiency and reducing downtime.
3. Integration with Environmental Monitoring Systems
With increasing global focus on environmental sustainability, AIS is being integrated with systems designed to monitor and reduce the environmental impact of shipping. For example, AIS data can track ships in Emission Control Areas (ECAs) and ensure compliance with International Maritime Organization (IMO) regulations regarding sulfur emissions and ballast water management. In the future, AIS could be used to verify adherence to green shipping practices, such as optimized speed for fuel efficiency and reduced carbon emissions.

7
AIS and Global Maritime Security
As maritime trade continues to expand, security remains a pressing issue. AIS is instrumental in maritime security operations, assisting in the identification and tracking of vessels across international waters. Its role in preventing illegal activities, such as smuggling, piracy, and illegal fishing, cannot be overstated.
1. Anti-Piracy Efforts
AIS provides critical data that helps authorities identify vessels in regions known for piracy, such as the Horn of Africa and the Strait of Malacca. By tracking ships in real time, authorities can respond quickly to distress signals and coordinate rescue efforts. However, in high-risk areas, ships may turn off their AIS transponders to avoid detection by pirates, which presents a challenge to maritime security forces.
2. Combatting Illegal Fishing
AIS is used to monitor fishing vessels and ensure they are operating within legal boundaries. Authorities use AIS data to track fishing fleets and spot any vessels that may be engaging in illegal, unreported, or unregulated (IUU) fishing. This is particularly important in Marine Protected Areas (MPAs), where fishing is often restricted to preserve marine ecosystems.
3. Border Security and Surveillance
Coastal states use AIS data for border security, monitoring vessels that approach or enter their territorial waters. AIS helps identify ships that may be carrying contraband, weapons, or unauthorized passengers. This technology plays a vital role in preventing human trafficking and the smuggling of illegal goods.

8
Conclusion
The Automatic Identification System (AIS) is a transformative tool that enhances maritime safety, operational efficiency, and global security. From preventing collisions to streamlining port operations and aiding in environmental protection, AIS has become indispensable in modern maritime operations. Its role in supporting autonomous ships, big data analytics, and future maritime innovations ensures that AIS will remain a cornerstone of the global shipping industry for years to come.
While AIS brings numerous benefits, challenges like signal congestion, data vulnerabilities, and over-reliance on the system must be carefully managed. As technology evolves, AIS will continue to adapt, integrating with emerging systems to ensure safer, more efficient, and environmentally responsible maritime operations.
While AIS brings numerous benefits, challenges like signal congestion, data vulnerabilities, and over-reliance on the system must be carefully managed. As technology evolves, AIS will continue to adapt, integrating with emerging systems to ensure safer, more efficient, and environmentally responsible maritime operations.

9
FAQs
1. What is the primary purpose of AIS?
The Automatic Identification System (AIS) is designed to enhance maritime safety by transmitting real-time information about a vessel's position, speed, course, and other details to nearby ships and coastal authorities. This helps avoid collisions, ensures smooth traffic management, and improves overall navigational safety.
2. Who is required to use AIS?
AIS is mandatory for vessels over 300 gross tons on international voyages, cargo ships over 500 gross tons, and all passenger ships, as per the International Maritime Organization (IMO) regulations under the SOLAS convention. However, many smaller vessels, such as recreational boats, can voluntarily use AIS to increase safety.
3. What are the differences between Class A and Class B AIS systems?
Class A AIS is required for larger commercial vessels and provides more frequent and detailed data, including faster update rates and higher transmission power. Class B AIS, used mainly by smaller recreational or fishing vessels, transmits at lower power with fewer updates and basic information.
4. How does AIS help prevent collisions?
AIS continuously broadcasts a ship’s position, speed, and course to other vessels within range. By displaying this information on navigation systems like ECDIS, mariners can track nearby vessels, predict potential collision points, and take corrective action early to avoid accidents.
5. Can AIS signals be turned off?
Yes, AIS transponders can be switched off, particularly in high-risk areas where ships want to avoid detection, such as regions with piracy threats. However, this action reduces situational awareness for other vessels and authorities, which can increase the risk of collisions or other incidents.